In short, maintaining patient confidentiality is your responsibility to ensure that a patient’s personal, medical, and treatment-related information is never shared improperly, intentionally or accidentally.
This article will explain what patient confidentiality is, why it matters, the laws that govern it, and how you, as a nursing assistant, can uphold it in daily practice. By the end of this guide, you’ll understand the best practices to safeguard patient information, the legal frameworks that regulate confidentiality, the common mistakes that lead to breaches, and the role of technology in data security.
What is Patient Confidentiality?
Patient confidentiality refers to the legal and ethical obligation of healthcare professionals to keep a patient’s personal and medical details private. This applies to any form of identifiable patient information, including:
- Medical history and diagnoses
- Treatment plans and prescriptions
- Contact details and personal identifiers
- Conversations between patients and healthcare providers
A patient’s trust in healthcare services depends on this principle. If they feel their information might be misused or shared without consent, they may withhold critical details that could impact their treatment.
In the UK, patient confidentiality is governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the NHS Code of Confidentiality. These guidelines set clear standards for handling sensitive health information.
Why is Patient Confidentiality Important?
Confidentiality directly impacts patient well-being and trust in the healthcare system. Here’s why it matters:
1. Protecting Patient Dignity
Health conditions can be deeply personal, and no one wants their medical history exposed to strangers. Confidentiality ensures that patients receive care without fear of embarrassment or stigma.
2. Building Trust in Healthcare Providers
Patients are more likely to be honest about their symptoms and history when they know their information is secure. This openness leads to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment outcomes.
3. Preventing Legal and Ethical Violations
Failure to maintain confidentiality can lead to legal action, loss of professional credibility, and fines. Even accidental breaches can have serious repercussions for both individuals and healthcare institutions.
4. Avoiding Discrimination and Harm
A breach of medical confidentiality could lead to discrimination in employment, insurance, or social settings. Patients may suffer real-world consequences if their health conditions are improperly disclosed.
Legal Regulations Governing Patient Confidentiality
1. The Data Protection Act 2018 & GDPR
The Data Protection Act 2018, which incorporates GDPR, requires healthcare providers to handle patient information lawfully and transparently. It gives patients control over their personal data and imposes strict penalties for breaches.
2. The NHS Confidentiality Code of Practice
This policy outlines best practices for handling patient information within the National Health Service (NHS), ensuring compliance with confidentiality laws.
3. The Health and Social Care Act 2012
This legislation emphasises the security of patient information across healthcare institutions and mandates proper data-sharing protocols.
Violating these laws can result in severe penalties, including termination of employment and legal action against both individuals and organisations.
How Nursing Assistants Can Protect Patient Confidentiality
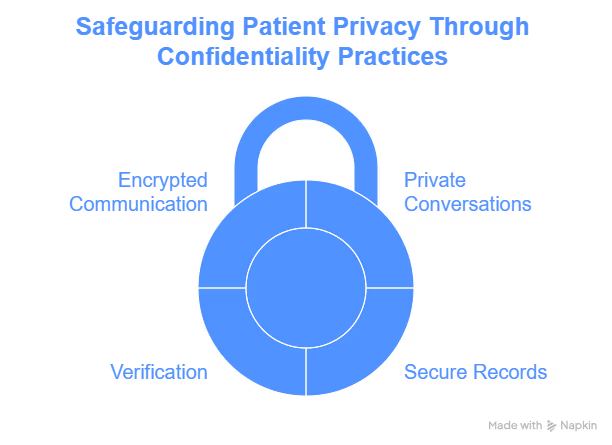
As a nursing assistant, you are directly involved in patient care, which means you have access to confidential information daily. Here are a few ways you can protect it:
1. Keep Conversations Private
- Never discuss patient details in public spaces like hallways, cafeterias, or reception areas.
- Lower your voice when discussing sensitive information, even in clinical settings.
2. Handle Patient Records Securely
- Always store physical records in locked cabinets when not in use.
- Log out of electronic systems after accessing patient files.
3. Verify Before Sharing
- Confirm the identity of the person requesting patient information.
- Never share patient details without proper authorisation.
4. Use Encrypted Communication
- Avoid using personal devices for work-related communication.
- Send patient details only through secure, authorised channels.
If you are interested in learning, you can check out our Healthcare GDPR Basics course.
Common Mistakes That Lead to Confidentiality Breaches
Even with the best intentions, there’s no escaping mistakes every now and then. Find out some common ways confidentiality is unintentionally violated below:
- Speaking Too Loudly in Shared Spaces – Even discussing a patient’s name in a waiting area can be overheard.
- Leaving Patient Records Unattended – Open charts, computer screens, or documents can be seen by unauthorised people.
- Using Personal Devices for Patient Data – Sending a quick email from your phone can expose information to security risks.
- Accessing Records Without Authorization – Even if you’re curious, looking at a patient’s file without need-to-know access is a breach of trust.
The Role of Technology in Protecting Confidentiality
With healthcare moving towards electronic health records (EHRs), patient data security has become critical. While digital records improve efficiency, they also introduce risks such as:
- Cybersecurity Threats – Hackers targeting sensitive health data.
- Unauthorised Access – Weak passwords or improper access permissions.
- Accidental Sharing – Emails sent to the wrong recipient.
To stay secure, ensure that:
✔ Systems are protected with strong passwords and multi-factor authentication.
✔ Data is shared only through secure, encrypted networks.
✔ Personal devices are not used for storing or sending patient information.
When is it Acceptable to Break Confidentiality?
While confidentiality is necessary, there are circumstances where it must be overridden for the greater good. These include:
- If a patient is at risk of harming themselves or others.
- If required by law (e.g., a court order or police investigation).
- If reporting suspected abuse or neglect.
In these cases, always follow your facility’s reporting procedures and consult with senior healthcare staff before taking action.
What Happens if a Breach Occurs?
If you witness or suspect a breach:
- Report It Immediately – Notify your supervisor or the compliance team.
- Document the Incident – Write down what happened, including dates and individuals involved.
- Follow Organizational Policies – Every healthcare facility has a set process for handling breaches.
Ignoring a breach can make the situation worse, so always act quickly.
FAQ
1. What is considered a breach of patient confidentiality?
Any unauthorised access, sharing, or discussion of a patient’s private information.
2. Can I share patient details with family members?
Not without the patient’s explicit consent, unless required by law.
3. What should I do if I accidentally disclose patient information?
Report it immediately to your supervisor to prevent further exposure.
4. How do electronic health records impact confidentiality?
EHRs streamline information access but require strict cybersecurity measures to prevent breaches.
5. What are the consequences of violating patient confidentiality?
Consequences range from disciplinary action to job termination and legal penalties.
Conclusion
As a nursing assistant, protecting patient confidentiality is one of your most important responsibilities. It not only builds trust with patients but also protects their dignity and legal rights. By following best practices, staying informed about legal requirements, and ensuring the secure handling of patient information, you contribute to a safe and ethical healthcare environment.



 " alt="10 Must-Know User Experience Design Tips for Better Products" />
" alt="10 Must-Know User Experience Design Tips for Better Products" />
 " alt="What Can You Do With a Level 3 Diploma in Health and Social Care?" />
" alt="What Can You Do With a Level 3 Diploma in Health and Social Care?" />
 " alt="Health & Social Care Qualifications: Your Most Asked Questions, Answered" />
" alt="Health & Social Care Qualifications: Your Most Asked Questions, Answered" />

